The Foxes and Rabbits Simulator
Nama : Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari
NRP : 05111740000010
Kelas : PBO-B
Berikut hasil dari tampilan Rabbit and Foxes Project:
NRP : 05111740000010
Kelas : PBO-B
The Foxes and Rabbits Simulator
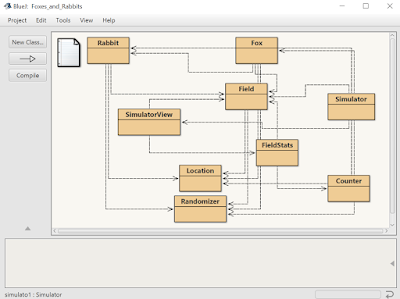
Kali ini saya akan membuat fox and rabbit project dengan menggunakan BlueJ. Berikut source code dan tampilan akhirnya. Yang kita butuhkan yaitu kelas :
1. Simulator
2. SimulatorView
3. FieldStats
4. Counter
5. Field
6. Location
7. Fox
8. Rabbit
9. Randomizer
- Berikut ini adalah Gambar untuk tampilan "Fox and Rabbit"
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Simulator
import java.util.Random; import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.awt.Color; /** * A simple predator-prey simulator, based on a rectangular field * containing rabbits and foxes. * @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSsari) * @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling) * @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018) */ public class Simulator { // Constants representing configuration information for the simulation. // The default width for the grid. private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 50; // The default depth of the grid. private static final int DEFAULT_DEPTH = 50; // The probability that a fox will be created in any given grid position. private static final double FOX_CREATION_PROBABILITY = 0.02; // The probability that a rabbit will be created in any given grid position. private static final double RABBIT_CREATION_PROBABILITY = 0.08; // Lists of animals in the field. Separate lists are kept for ease of iteration. private List<Rabbit> rabbits; private List<Fox> foxes; // The current state of the field. private Field field; // The current step of the simulation. private int step; // A graphical view of the simulation. private SimulatorView view; /** * Construct a simulation field with default size. */ public Simulator() { this(DEFAULT_DEPTH, DEFAULT_WIDTH); } /** * Create a simulation field with the given size. * @param depth Depth of the field. Must be greater than zero. * @param width Width of the field. Must be greater than zero. */ public Simulator(int depth, int width) { if(width <= 0 || depth <= 0) { System.out.println("The dimensions must be greater than zero."); System.out.println("Using default values."); depth = DEFAULT_DEPTH; width = DEFAULT_WIDTH; } rabbits = new ArrayList<Rabbit>(); foxes = new ArrayList<Fox>(); field = new Field(depth, width); // Create a view of the state of each location in the field. view = new SimulatorView(depth, width); view.setColor(Rabbit.class, Color.orange); view.setColor(Fox.class, Color.blue); // Setup a valid starting point. reset(); } /** * Run the simulation from its current state for a reasonably long period, * e.g. 500 steps. */ public void runLongSimulation() { simulate(500); } /** * Run the simulation from its current state for the given number of steps. * Stop before the given number of steps if it ceases to be viable. * @param numSteps The number of steps to run for. */ public void simulate(int numSteps) { for(int step = 1; step <= numSteps && view.isViable(field); step++) { simulateOneStep(); } } /** * Run the simulation from its current state for a single step. * Iterate over the whole field updating the state of each * fox and rabbit. */ public void simulateOneStep() { step++; // Provide space for newborn rabbits. List<Rabbit> newRabbits = new ArrayList<Rabbit>(); // Let all rabbits act. for(Iterator<Rabbit> it = rabbits.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { Rabbit rabbit = it.next(); rabbit.run(newRabbits); if(! rabbit.isAlive()) { it.remove(); } } // Provide space for newborn foxes. List<Fox> newFoxes = new ArrayList<Fox>(); // Let all foxes act. for(Iterator<Fox> it = foxes.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { Fox fox = it.next(); fox.hunt(newFoxes); if(! fox.isAlive()) { it.remove(); } } // Add the newly born foxes and rabbits to the main lists. rabbits.addAll(newRabbits); foxes.addAll(newFoxes); view.showStatus(step, field); } /** * Reset the simulation to a starting position. */ public void reset() { step = 0; rabbits.clear(); foxes.clear(); populate(); // Show the starting state in the view. view.showStatus(step, field); } /** * Randomly populate the field with foxes and rabbits. */ private void populate() { Random rand = Randomizer.getRandom(); field.clear(); for(int row = 0; row < field.getDepth(); row++) { for(int col = 0; col < field.getWidth(); col++) { if(rand.nextDouble() <= FOX_CREATION_PROBABILITY) { Location location = new Location(row, col); Fox fox = new Fox(true, field, location); foxes.add(fox); } else if(rand.nextDouble() <= RABBIT_CREATION_PROBABILITY) { Location location = new Location(row, col); Rabbit rabbit = new Rabbit(true, field, location); rabbits.add(rabbit); } // else leave the location empty. } } } }
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class SimulatorView
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* A graphical view of the simulation grid.
* The view displays a colored rectangle for each location
* representing its contents. It uses a default background color.
* Colors for each type of species can be defined using the
* setColor method.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class SimulatorView extends JFrame
{
// Colors used for empty locations.
private static final Color EMPTY_COLOR = Color.white;
// Color used for objects that have no defined color.
private static final Color UNKNOWN_COLOR = Color.gray;
private final String STEP_PREFIX = "Step: ";
private final String POPULATION_PREFIX = "Population: ";
private JLabel stepLabel, population;
private FieldView fieldView;
// A map for storing colors for participants in the simulation
private Map<Class, Color> colors;
// A statistics object computing and storing simulation information
private FieldStats stats;
/**
* Create a view of the given width and height.
* @param height The simulation's height.
* @param width The simulation's width.
*/
public SimulatorView(int height, int width)
{
stats = new FieldStats();
colors = new LinkedHashMap<Class, Color>();
setTitle("Fox and Rabbit Simulation");
stepLabel = new JLabel(STEP_PREFIX, JLabel.CENTER);
population = new JLabel(POPULATION_PREFIX, JLabel.CENTER);
setLocation(100, 50);
fieldView = new FieldView(height, width);
Container contents = getContentPane();
contents.add(stepLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
contents.add(fieldView, BorderLayout.CENTER);
contents.add(population, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
/**
* Define a color to be used for a given class of animal.
* @param animalClass The animal's Class object.
* @param color The color to be used for the given class.
*/
public void setColor(Class animalClass, Color color)
{
colors.put(animalClass, color);
}
/**
* @return The color to be used for a given class of animal.
*/
private Color getColor(Class animalClass)
{
Color col = colors.get(animalClass);
if(col == null) {
// no color defined for this class
return UNKNOWN_COLOR;
}
else {
return col;
}
}
/**
* Show the current status of the field.
* @param step Which iteration step it is.
* @param field The field whose status is to be displayed.
*/
public void showStatus(int step, Field field)
{
if(!isVisible()) {
setVisible(true);
}
stepLabel.setText(STEP_PREFIX + step);
stats.reset();
fieldView.preparePaint();
for(int row = 0; row < field.getDepth(); row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < field.getWidth(); col++) {
Object animal = field.getObjectAt(row, col);
if(animal != null) {
stats.incrementCount(animal.getClass());
fieldView.drawMark(col, row, getColor(animal.getClass()));
}
else {
fieldView.drawMark(col, row, EMPTY_COLOR);
}
}
}
stats.countFinished();
population.setText(POPULATION_PREFIX + stats.getPopulationDetails(field));
fieldView.repaint();
}
/**
* Determine whether the simulation should continue to run.
* @return true If there is more than one species alive.
*/
public boolean isViable(Field field)
{
return stats.isViable(field);
}
/**
* Provide a graphical view of a rectangular field. This is
* a nested class (a class defined inside a class) which
* defines a custom component for the user interface. This
* component displays the field.
* This is rather advanced GUI stuff - you can ignore this
* for your project if you like.
*/
private class FieldView extends JPanel
{
private final int GRID_VIEW_SCALING_FACTOR = 6;
private int gridWidth, gridHeight;
private int xScale, yScale;
Dimension size;
private Graphics g;
private Image fieldImage;
/**
* Create a new FieldView component.
*/
public FieldView(int height, int width)
{
gridHeight = height;
gridWidth = width;
size = new Dimension(0, 0);
}
/**
* Tell the GUI manager how big we would like to be.
*/
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(gridWidth * GRID_VIEW_SCALING_FACTOR,
gridHeight * GRID_VIEW_SCALING_FACTOR);
}
/**
* Prepare for a new round of painting. Since the component
* may be resized, compute the scaling factor again.
*/
public void preparePaint()
{
if(! size.equals(getSize())) { // if the size has changed...
size = getSize();
fieldImage = fieldView.createImage(size.width, size.height);
g = fieldImage.getGraphics();
xScale = size.width / gridWidth;
if(xScale < 1) {
xScale = GRID_VIEW_SCALING_FACTOR;
}
yScale = size.height / gridHeight;
if(yScale < 1) {
yScale = GRID_VIEW_SCALING_FACTOR;
}
}
}
/**
* Paint on grid location on this field in a given color.
*/
public void drawMark(int x, int y, Color color)
{
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(x * xScale, y * yScale, xScale-1, yScale-1);
}
/**
* The field view component needs to be redisplayed. Copy the
* internal image to screen.
*/
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
if(fieldImage != null) {
Dimension currentSize = getSize();
if(size.equals(currentSize)) {
g.drawImage(fieldImage, 0, 0, null);
}
else {
// Rescale the previous image.
g.drawImage(fieldImage, 0, 0, currentSize.width, currentSize.height, null);
}
}
}
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class FieldStats
import java.awt.Color;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* This class collects and provides some statistical data on the state
* of a field. It is flexible: it will create and maintain a counter
* for any class of object that is found within the field.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class FieldStats
{
// Counters for each type of entity (fox, rabbit, etc.) in the simulation.
private HashMap<Class, Counter> counters;
// Whether the counters are currently up to date.
private boolean countsValid;
/**
* Construct a FieldStats object.
*/
public FieldStats()
{
// Set up a collection for counters for each type of animal that
// we might find
counters = new HashMap<Class, Counter>();
countsValid = true;
}
/**
* Get details of what is in the field.
* @return A string describing what is in the field.
*/
public String getPopulationDetails(Field field)
{
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
if(!countsValid) {
generateCounts(field);
}
for(Class key : counters.keySet()) {
Counter info = counters.get(key);
buffer.append(info.getName());
buffer.append(": ");
buffer.append(info.getCount());
buffer.append(' ');
}
return buffer.toString();
}
/**
* Invalidate the current set of statistics; reset all
* counts to zero.
*/
public void reset()
{
countsValid = false;
for(Class key : counters.keySet()) {
Counter count = counters.get(key);
count.reset();
}
}
/**
* Increment the count for one class of animal.
* @param animalClass The class of animal to increment.
*/
public void incrementCount(Class animalClass)
{
Counter count = counters.get(animalClass);
if(count == null) {
// We do not have a counter for this species yet.
// Create one.
count = new Counter(animalClass.getName());
counters.put(animalClass, count);
}
count.increment();
}
/**
* Indicate that an animal count has been completed.
*/
public void countFinished()
{
countsValid = true;
}
/**
* Determine whether the simulation is still viable.
* I.e., should it continue to run.
* @return true If there is more than one species alive.
*/
public boolean isViable(Field field)
{
// How many counts are non-zero.
int nonZero = 0;
if(!countsValid) {
generateCounts(field);
}
for(Class key : counters.keySet()) {
Counter info = counters.get(key);
if(info.getCount() > 0) {
nonZero++;
}
}
return nonZero > 1;
}
/**
* Generate counts of the number of foxes and rabbits.
* These are not kept up to date as foxes and rabbits
* are placed in the field, but only when a request
* is made for the information.
* @param field The field to generate the stats for.
*/
private void generateCounts(Field field)
{
reset();
for(int row = 0; row < field.getDepth(); row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < field.getWidth(); col++) {
Object animal = field.getObjectAt(row, col);
if(animal != null) {
incrementCount(animal.getClass());
}
}
}
countsValid = true;
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah source code untuk Class counter
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* Provide a counter for a participant in the simulation.
* This includes an identifying string and a count of how
* many participants of this type currently exist within
* the simulation.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSsari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Counter
{
// A name for this type of simulation participant
private String name;
// How many of this type exist in the simulation.
private int count;
/**
* Provide a name for one of the simulation types.
* @param name A name, e.g. "Fox".
*/
public Counter(String name)
{
this.name = name;
count = 0;
}
/**
* @return The short description of this type.
*/
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
/**
* @return The current count for this type.
*/
public int getCount()
{
return count;
}
/**
* Increment the current count by one.
*/
public void increment()
{
count++;
}
/**
* Reset the current count to zero.
*/
public void reset()
{
count = 0;
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Field
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Represent a rectangular grid of field positions.
* Each position is able to store a single animal.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya,19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Field
{
// A random number generator for providing random locations.
private static final Random rand = Randomizer.getRandom();
// The depth and width of the field.
private int depth, width;
// Storage for the animals.
private Object[][] field;
/**
* Represent a field of the given dimensions.
* @param depth The depth of the field.
* @param width The width of the field.
*/
public Field(int depth, int width)
{
this.depth = depth;
this.width = width;
field = new Object[depth][width];
}
/**
* Empty the field.
*/
public void clear()
{
for(int row = 0; row < depth; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
field[row][col] = null;
}
}
}
/**
* Clear the given location.
* @param location The location to clear.
*/
public void clear(Location location)
{
field[location.getRow()][location.getCol()] = null;
}
/**
* Place an animal at the given location.
* If there is already an animal at the location it will
* be lost.
* @param animal The animal to be placed.
* @param row Row coordinate of the location.
* @param col Column coordinate of the location.
*/
public void place(Object animal, int row, int col)
{
place(animal, new Location(row, col));
}
/**
* Place an animal at the given location.
* If there is already an animal at the location it will
* be lost.
* @param animal The animal to be placed.
* @param location Where to place the animal.
*/
public void place(Object animal, Location location)
{
field[location.getRow()][location.getCol()] = animal;
}
/**
* Return the animal at the given location, if any.
* @param location Where in the field.
* @return The animal at the given location, or null if there is none.
*/
public Object getObjectAt(Location location)
{
return getObjectAt(location.getRow(), location.getCol());
}
/**
* Return the animal at the given location, if any.
* @param row The desired row.
* @param col The desired column.
* @return The animal at the given location, or null if there is none.
*/
public Object getObjectAt(int row, int col)
{
return field[row][col];
}
/**
* Generate a random location that is adjacent to the
* given location, or is the same location.
* The returned location will be within the valid bounds
* of the field.
* @param location The location from which to generate an adjacency.
* @return A valid location within the grid area.
*/
public Location randomAdjacentLocation(Location location)
{
List<Location> adjacent = adjacentLocations(location);
return adjacent.get(0);
}
/**
* Get a shuffled list of the free adjacent locations.
* @param location Get locations adjacent to this.
* @return A list of free adjacent locations.
*/
public List<Location> getFreeAdjacentLocations(Location location)
{
List<Location> free = new LinkedList<Location>();
List<Location> adjacent = adjacentLocations(location);
for(Location next : adjacent) {
if(getObjectAt(next) == null) {
free.add(next);
}
}
return free;
}
/**
* Try to find a free location that is adjacent to the
* given location. If there is none, return null.
* The returned location will be within the valid bounds
* of the field.
* @param location The location from which to generate an adjacency.
* @return A valid location within the grid area.
*/
public Location freeAdjacentLocation(Location location)
{
// The available free ones.
List<Location> free = getFreeAdjacentLocations(location);
if(free.size() > 0) {
return free.get(0);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Return a shuffled list of locations adjacent to the given one.
* The list will not include the location itself.
* All locations will lie within the grid.
* @param location The location from which to generate adjacencies.
* @return A list of locations adjacent to that given.
*/
public List<Location> adjacentLocations(Location location)
{
assert location != null : "Null location passed to adjacentLocations";
// The list of locations to be returned.
List<Location> locations = new LinkedList<Location>();
if(location != null) {
int row = location.getRow();
int col = location.getCol();
for(int roffset = -1; roffset <= 1; roffset++) {
int nextRow = row + roffset;
if(nextRow >= 0 && nextRow < depth) {
for(int coffset = -1; coffset <= 1; coffset++) {
int nextCol = col + coffset;
// Exclude invalid locations and the original location.
if(nextCol >= 0 && nextCol < width && (roffset != 0 || coffset != 0)) {
locations.add(new Location(nextRow, nextCol));
}
}
}
}
// Shuffle the list. Several other methods rely on the list
// being in a random order.
Collections.shuffle(locations, rand);
}
return locations;
}
/**
* Return the depth of the field.
* @return The depth of the field.
*/
public int getDepth()
{
return depth;
}
/**
* Return the width of the field.
* @return The width of the field.
*/
public int getWidth()
{
return width;
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Location
/**
* Represent a location in a rectangular grid.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Location
{
// Row and column positions.
private int row;
private int col;
/**
* Represent a row and column.
* @param row The row.
* @param col The column.
*/
public Location(int row, int col)
{
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
/**
* Implement content equality.
*/
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(obj instanceof Location) {
Location other = (Location) obj;
return row == other.getRow() && col == other.getCol();
}
else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Return a string of the form row,column
* @return A string representation of the location.
*/
public String toString()
{
return row + "," + col;
}
/**
* Use the top 16 bits for the row value and the bottom for
* the column. Except for very big grids, this should give a
* unique hash code for each (row, col) pair.
* @return A hashcode for the location.
*/
public int hashCode()
{
return (row << 16) + col;
}
/**
* @return The row.
*/
public int getRow()
{
return row;
}
/**
* @return The column.
*/
public int getCol()
{
return col;
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Fox
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* A simple model of a fox.
* Foxes age, move, eat rabbits, and die.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Fox
{
// Characteristics shared by all foxes (static fields).
// The age at which a fox can start to breed.
private static final int BREEDING_AGE = 10;
// The age to which a fox can live.
private static final int MAX_AGE = 150;
// The likelihood of a fox breeding.
private static final double BREEDING_PROBABILITY = 0.35;
// The maximum number of births.
private static final int MAX_LITTER_SIZE = 5;
// The food value of a single rabbit. In effect, this is the
// number of steps a fox can go before it has to eat again.
private static final int RABBIT_FOOD_VALUE = 7;
// A shared random number generator to control breeding.
private static final Random rand = Randomizer.getRandom();
// Individual characteristics (instance fields).
// The fox's age.
private int age;
// Whether the fox is alive or not.
private boolean alive;
// The fox's position.
private Location location;
// The field occupied.
private Field field;
// The fox's food level, which is increased by eating rabbits.
private int foodLevel;
/**
* Create a fox. A fox can be created as a new born (age zero
* and not hungry) or with a random age and food level.
*
* @param randomAge If true, the fox will have random age and hunger level.
* @param field The field currently occupied.
* @param location The location within the field.
*/
public Fox(boolean randomAge, Field field, Location location)
{
age = 0;
alive = true;
this.field = field;
setLocation(location);
if(randomAge) {
age = rand.nextInt(MAX_AGE);
foodLevel = rand.nextInt(RABBIT_FOOD_VALUE);
}
else {
// leave age at 0
foodLevel = RABBIT_FOOD_VALUE;
}
}
/**
* This is what the fox does most of the time: it hunts for
* rabbits. In the process, it might breed, die of hunger,
* or die of old age.
* @param field The field currently occupied.
* @param newFoxes A list to add newly born foxes to.
*/
public void hunt(List<Fox> newFoxes)
{
incrementAge();
incrementHunger();
if(alive) {
giveBirth(newFoxes);
// Move towards a source of food if found.
Location newLocation = findFood(location);
if(newLocation == null) {
// No food found - try to move to a free location.
newLocation = field.freeAdjacentLocation(location);
}
// See if it was possible to move.
if(newLocation != null) {
setLocation(newLocation);
}
else {
// Overcrowding.
setDead();
}
}
}
/**
* Check whether the fox is alive or not.
* @return True if the fox is still alive.
*/
public boolean isAlive()
{
return alive;
}
/**
* Return the fox's location.
* @return The fox's location.
*/
public Location getLocation()
{
return location;
}
/**
* Place the fox at the new location in the given field.
* @param newLocation The fox's new location.
*/
private void setLocation(Location newLocation)
{
if(location != null) {
field.clear(location);
}
location = newLocation;
field.place(this, newLocation);
}
/**
* Increase the age. This could result in the fox's death.
*/
private void incrementAge()
{
age++;
if(age > MAX_AGE) {
setDead();
}
}
/**
* Make this fox more hungry. This could result in the fox's death.
*/
private void incrementHunger()
{
foodLevel--;
if(foodLevel <= 0) {
setDead();
}
}
/**
* Tell the fox to look for rabbits adjacent to its current location.
* Only the first live rabbit is eaten.
* @param location Where in the field it is located.
* @return Where food was found, or null if it wasn't.
*/
private Location findFood(Location location)
{
List<Location> adjacent = field.adjacentLocations(location);
Iterator<Location> it = adjacent.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Location where = it.next();
Object animal = field.getObjectAt(where);
if(animal instanceof Rabbit) {
Rabbit rabbit = (Rabbit) animal;
if(rabbit.isAlive()) {
rabbit.setDead();
foodLevel = RABBIT_FOOD_VALUE;
// Remove the dead rabbit from the field.
return where;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Check whether or not this fox is to give birth at this step.
* New births will be made into free adjacent locations.
* @param newFoxes A list to add newly born foxes to.
*/
private void giveBirth(List<Fox> newFoxes)
{
// New foxes are born into adjacent locations.
// Get a list of adjacent free locations.
List<Location> free = field.getFreeAdjacentLocations(location);
int births = breed();
for(int b = 0; b < births && free.size() > 0; b++) {
Location loc = free.remove(0);
Fox young = new Fox(false, field, loc);
newFoxes.add(young);
}
}
/**
* Generate a number representing the number of births,
* if it can breed.
* @return The number of births (may be zero).
*/
private int breed()
{
int births = 0;
if(canBreed() && rand.nextDouble() <= BREEDING_PROBABILITY) {
births = rand.nextInt(MAX_LITTER_SIZE) + 1;
}
return births;
}
/**
* A fox can breed if it has reached the breeding age.
*/
private boolean canBreed()
{
return age >= BREEDING_AGE;
}
/**
* Indicate that the fox is no longer alive.
* It is removed from the field.
*/
private void setDead()
{
alive = false;
if(location != null) {
field.clear(location);
location = null;
field = null;
}
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Rabbit
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* A simple model of a rabbit.
* Rabbits age, move, breed, and die.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Rabbit
{
// Characteristics shared by all rabbits (static fields).
// The age at which a rabbit can start to breed.
private static final int BREEDING_AGE = 5;
// The age to which a rabbit can live.
private static final int MAX_AGE = 40;
// The likelihood of a rabbit breeding.
private static final double BREEDING_PROBABILITY = 0.15;
// The maximum number of births.
private static final int MAX_LITTER_SIZE = 4;
// A shared random number generator to control breeding.
private static final Random rand = Randomizer.getRandom();
// Individual characteristics (instance fields).
// The rabbit's age.
private int age;
// Whether the rabbit is alive or not.
private boolean alive;
// The rabbit's position.
private Location location;
// The field occupied.
private Field field;
/**
* Create a new rabbit. A rabbit may be created with age
* zero (a new born) or with a random age.
*
* @param randomAge If true, the rabbit will have a random age.
* @param field The field currently occupied.
* @param location The location within the field.
*/
public Rabbit(boolean randomAge, Field field, Location location)
{
age = 0;
alive = true;
this.field = field;
setLocation(location);
if(randomAge) {
age = rand.nextInt(MAX_AGE);
}
}
/**
* This is what the rabbit does most of the time - it runs
* around. Sometimes it will breed or die of old age.
* @param newRabbits A list to add newly born rabbits to.
*/
public void run(List<Rabbit> newRabbits)
{
incrementAge();
if(alive) {
giveBirth(newRabbits);
// Try to move into a free location.
Location newLocation = field.freeAdjacentLocation(location);
if(newLocation != null) {
setLocation(newLocation);
}
else {
// Overcrowding.
setDead();
}
}
}
/**
* Check whether the rabbit is alive or not.
* @return true if the rabbit is still alive.
*/
public boolean isAlive()
{
return alive;
}
/**
* Indicate that the rabbit is no longer alive.
* It is removed from the field.
*/
public void setDead()
{
alive = false;
if(location != null) {
field.clear(location);
location = null;
field = null;
}
}
/**
* Return the rabbit's location.
* @return The rabbit's location.
*/
public Location getLocation()
{
return location;
}
/**
* Place the rabbit at the new location in the given field.
* @param newLocation The rabbit's new location.
*/
private void setLocation(Location newLocation)
{
if(location != null) {
field.clear(location);
}
location = newLocation;
field.place(this, newLocation);
}
/**
* Increase the age.
* This could result in the rabbit's death.
*/
private void incrementAge()
{
age++;
if(age > MAX_AGE) {
setDead();
}
}
/**
* Check whether or not this rabbit is to give birth at this step.
* New births will be made into free adjacent locations.
* @param newRabbits A list to add newly born rabbits to.
*/
private void giveBirth(List<Rabbit> newRabbits)
{
// New rabbits are born into adjacent locations.
// Get a list of adjacent free locations.
List<Location> free = field.getFreeAdjacentLocations(location);
int births = breed();
for(int b = 0; b < births && free.size() > 0; b++) {
Location loc = free.remove(0);
Rabbit young = new Rabbit(false, field, loc);
newRabbits.add(young);
}
}
/**
* Generate a number representing the number of births,
* if it can breed.
* @return The number of births (may be zero).
*/
private int breed()
{
int births = 0;
if(canBreed() && rand.nextDouble() <= BREEDING_PROBABILITY) {
births = rand.nextInt(MAX_LITTER_SIZE) + 1;
}
return births;
}
/**
* A rabbit can breed if it has reached the breeding age.
* @return true if the rabbit can breed, false otherwise.
*/
private boolean canBreed()
{
return age >= BREEDING_AGE;
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah Source Code untuk Class Randomizer
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Provide control over the randomization of the simulation.
* @author (Isnaini Nurul KurniaSari)
* @credits (David J. Barnes and Michael Kolling)
* @version (Surabaya, 19 Nopember 2018)
*/
public class Randomizer
{
// The default seed for control of randomization.
private static final int SEED = 1111;
// A shared Random object, if required.
private static final Random rand = new Random(SEED);
// Determine whether a shared random generator is to be provided.
private static final boolean useShared = true;
/**
* Constructor for objects of class Randomizer
*/
public Randomizer()
{
}
/**
* Provide a random generator.
* @return A random object.
*/
public static Random getRandom()
{
if(useShared) {
return rand;
}
else {
return new Random();
}
}
/**
}
* Reset the randomization.
* This will have no effect if randomization is not through
* a shared Random generator.
*/
public static void reset()
{
if(useShared) {
rand.setSeed(SEED);
}
}
- Berikut ini adalah hasil tampilan dari Foxes and Rabbits projectnew Simulator() berfungsi untuk memulai simulator dengan panjang dan lebar field masing-masing 50
- Untuk mensimulasikan foxes and rabbits sebanyak satu step maka gunakan :
- Hasil dari tampilan Rabbit and Foxes Project:
- untuk memulai simulator dengan panjang dan lebar field yang dapat ditentukan sendiri maka kita menggunakan fungsi new Simulator(int depth, int width)
- Berikut hasil dari tampilan Rabbit and Foxes Project:
- Untuk mensimulasikan foxes and rabbits sebanyak 500 steps kita menggunakan:
-Terima Kasih, Semoga Bermanfaat-












Comments
Post a Comment